Transtheoretical Model of Change

What is TTM?
Transtheoretical Model of Change (henceforth, TTM) is focused on the stages and aspects of behavioral change and places personal changes in the societal and institutional contexts.
The TTM of Change
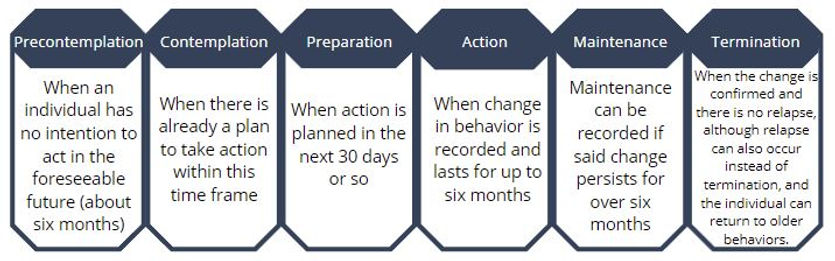
The comprehensive "transtheoretical Model (TTM) uses stages of change to integrate processes and principles of change across major theories of intervention," and can prove useful in understanding change in complex situations (Prochaska, Redding, & Evers, 215, p.125). It reveals the following six stages:
At each stage, different processes of change can be observed, including:

Origins of TTM
Originating in health sciences, TTM stemmed from a series of studies about individuals who tried to quit smoking and emerged as a comprehensive model of intentional behavioral change. Over the years the TTM has often been used in other disciplines as well, including LIS.
Original studies:
Prochaska, J. O., & DiClemente, C. C. (1983). Stages and processes of self-change of
smoking: Toward an integrative model of change. Journal of Consulting and Clinical
Psychology, 51(3), 390–395.
Prochaska, J. O., Redding, C. A., & Evers, K. E. (2016). The transtheoretical model and
stages of change. In K. Glanz, B. K. Rimer, & K. Viswanath (Eds.) (5th ed., Vol. 4.
Health behavior: Theory, research, and practice (pp. 125–148). San Francisco, CA:
Jossey-Bass.
Mapping the Study Findings to the TTM Concepts
Increased awareness of the causes and consequences of certain behaviors
Cognitive learning: awareness
“It made me aware of other issues affecting people of color in academic libraries especially those considered 'staff'”
Dramatic relief, driven by positive or negative feelings that motivate people to act
Affective learning: emotion
“I had just never seen 300 women in one space. And then, to see the sea of diverse faces was inspiring.” “It made me angry at my institution.”
Self-reevaluation
Personal learning and change: self-awareness and self-improvement
“I was uncomfortable when I realized that I had done some of things that were perceived as threatening.” “It made me realize the need to make others aware and to understand that not everyone experiences life the way I do”
Environmental reevaluation, including impact on others
Self-liberation tied
into the belief in the possibility of change and commitment
to change
Helping relationships
Behavioral learning: action
“[Professional practices have changed] [s]ignificantly. Re-evaluated our values, made our value statements clear, started programs that are still ongoing. We are committed and want to demonstrate our commitment with our behaviors and actions.”
Personal learning and change: self-awareness and self-improvement
“Got me even more fired up to integrate and advocate for these issues at my institution.”
Social learning: interaction
“I felt like there were more people involved in this work than I had thought. This isn’t really a subtopic of librarianship anymore, it's increasingly a central part of the discourse of our profession”
Social liberation resulting in opportunities and alternatives for changed behaviors
Affective learning: emotion
“It made me both hopeful because of the amazing people doing the work that I meant and worried because of the sheer amount of work that still needed to be done.”
Counterconditioning or adoption of improved behaviors
Behavioral learning: action
“Our institution is committed to asking questions about our practices in a DEI framework, so there’s good institutional support for this work. […] We do searches differently now - much more information is shared with candidates to enable them to shine rather than waste time together trying to figure out what we are looking for.”
Stimulus control or removing cues for problematic behaviors
Behavioral learning: action
“Comfort with old ways is the biggest obstacle - people sometimes feel like supporting DEI work is “one more thing,” so the challenge is shifting the frame to articulate how it makes all of us, and all that we do, better and more accessible for all.”
Reinforcement manage-ment, tied into self-encouragement for making progress
Behavioral learning: action
"I was already trying to decolonize my collection practices before attending the event, but after attending the event I felt much more confident in my approach. I was confident enough to do a presentation to fellow librarians and answer questions.”



